- Home
- About Us
- Treatments
- Testimonials
- Media
- International Patient
- Blog
- Cases
- Contact
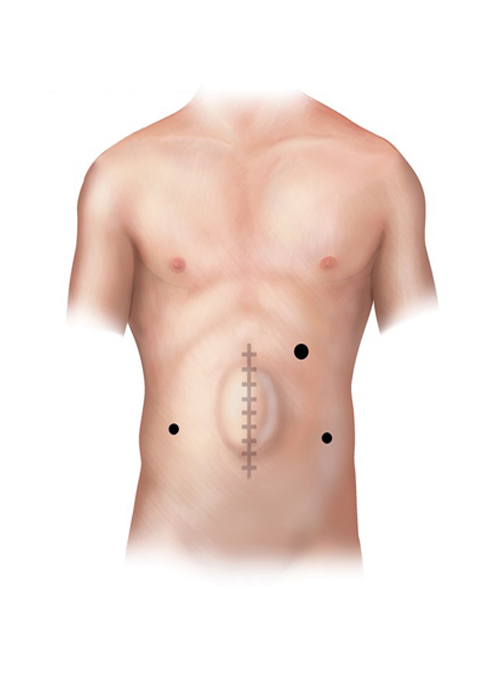
A ventral hernia is a bulge through an opening in the muscles on the abdomen. A hernia can occur at a past incision site (incisional), above the navel (epigastric), or other weak muscle sites (primary abdominal). Piles Doctor in Ahmedabad
Watchful waiting is an option for adults with hernias that are reducible and not uncomfortable.
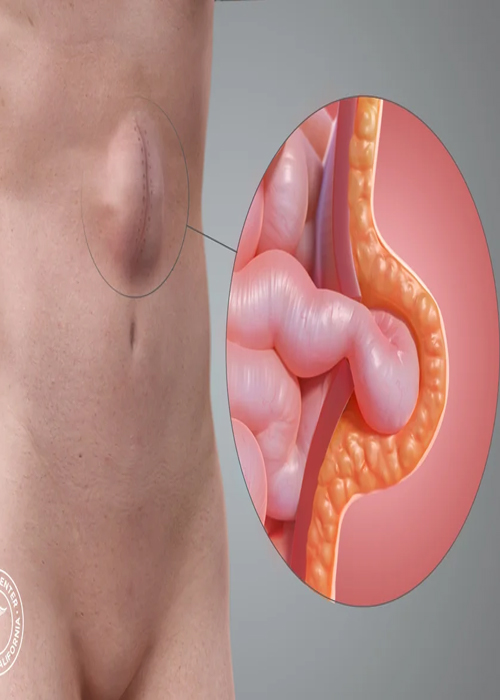
A ventral hernia is a bulge through an opening in the muscles on the abdomen. If a hernia reduces in size when a person is lying flat or in response to manual pressure, it is reducible. If it cannot be reduced, it is irreducible or incarcerated, and a portion of the intestine may be bulging through the hernia sac. A hernia is strangulated if the intestine is trapped in the hernia pouch and the blood supply to the intestine is decreased. This is a surgical emergency. A primary abdominal hernia occurs spontaneously in an area of natural weakness of the abdominal muscle. An incisional hernia bulges through a past incision site. This issue can be the result of scar tissue or weak muscles around the site. An epigastric hernia bulges midline above the umbilicus.
The most common symptoms of a hernia are:
The site is checked for a bulge.
They are also called ventral hernias. They can occur: Large hernia with loop of intestine
Incisional hernias can develop at the laparoscopic port site in 5 of 1,000 patients and in up to 150 of 1,000 patients who have had a prior open abdominal incision. Most appear in the first 5 years after an operation. Risk factors that can contribute to incisional hernia formation include:
The type of operation depends on the hernia size, location, and if it is a repeat hernia. Your health, age, anesthesia risk, and the surgeon’s expertise are also important. An operation is the only treatment for a hernia repair. Single Mesh Repair PL Sutured Muscle Repair
The surgeon makes an incision near the hernia site. The bulging tissue is gently pushed back into the abdomen. Sutures, mesh, or a tissue flap is used to close the muscle. With complex or large hernias, small drains may be placed going from inside to the outside of the abdomen. The site is closed using sutures, staples, or surgical glue.
The hernia sac is removed. Mesh is placed over the hernia site. The mesh is attached using sutures sewn into the stronger tissue surrounding the hernia site. Mesh is often used for large hernia repairs and may reduce the risk that a hernia will come back. The site is closed using sutures, staples, or surgical glue.
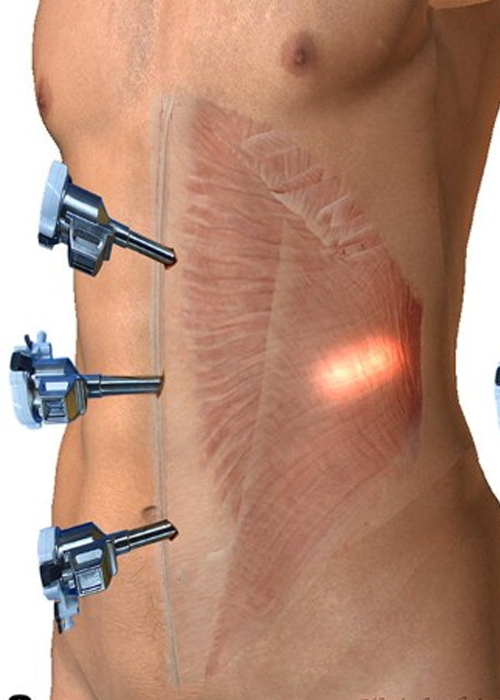
The surgeon will make several small punctures or incisions in the abdomen. Ports or trocars (hollow tubes) are inserted into the openings. Surgical tools are placed into the ports. The abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to make it easier for the surgeon to see a hernia. Mesh is sutured, stapled, or clipped to the muscle around the hernia site. The hernia site can also be sewn directly together.
There is no one type of repair that is good for all ventral hernias. Laparoscopic repairs are associated with lower infection rates and shorter hospital stays. There is no difference in recurrence rates, long-term pain, or quality of life. For patients with strangulated intestines and infections, the laparoscopic approach may not be an option.
Mesh reduces the risk that the hernia will return again. Mesh can be tacked, stapled, or sutured. Obesity and wound complications increase the risk of recurrence You may be placed on a weight loss, smoking cessation, or a diabetes control program before an elective repair to support the best outcome.
watchful waiting is an option for a hernia without symptoms. All patients should get treatment if they have sudden sharp abdominal pain and vomiting. These symptoms can indicate an incarcerated hernia and bowel obstruction Trusses or belts made to apply pressure to a hernia require correct fitting. When used correctly, part or complete control of a hernia was achieved in 31% of patients, and 64% found the truss to be uncomfortable.

User visits the website and navigates to the "Appointment Booking" section.
After completing the form, the user submits their appointment request.
If the requested slot is available, the administrative staff confirms appointment.