- Home
- About Us
- Treatments
- Testimonials
- Media
- International Patient
- Blog
- Cases
- Contact
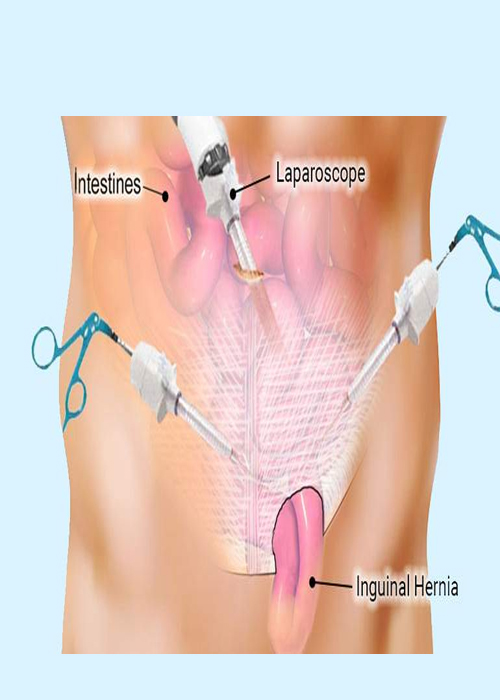
A hernia occurs when tissue bulges out through an opening in the muscles. Any part of the abdominal wall can weaken and develop a hernia, but the most common sites are the groin (inguinal), the navel (umbilical) and a previous surgical incision site. Piles Doctor in Ahmedabad
Watchful waiting is an option for adults with hernias that are reducible and not uncomfortable.
A groin hernia occurs when the intestine bulges through the opening in the muscle in the groin area. A reducible hernia can be pushed back into the opening. When intestine or abdominal tissue fills the hernia sac and cannot be pushed back, it is called irreducible or incarcerated. A hernia is strangulated if the intestine is trapped in the hernia pouch and the blood supply to the intestine is decreased. This is a surgical emergency. There are two types of groin hernias: An inguinal hernia appears as a bulge in the groin or scrotum. Inguinal hernias account for 75% of all hernias and are most common in men. A femoral hernia appears as a bulge in the groin, upper thigh, or labia (skin folds surrounding the vaginal opening). Femoral hernias are ten times more common in women. They are always repaired because of a high risk of strangulation. Herniorrhaphy is the surgical repair of a hernia. Hernioplasty is the surgical repair of a hernia with mesh.
The most common symptoms of a hernia are:
There may be no cause for a hernia. Some risk factors are:
that have symptoms similar to hernias include enlarged lymph nodes, cysts, and testicular problems such as scrotal hydrocele
The site is checked for a bulge.
Other tests may include:
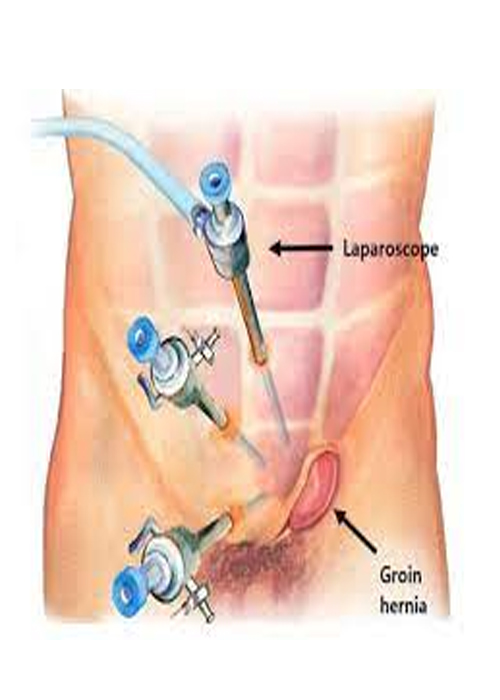
The type of operation depends on hernia size and location, and if it is a repeat hernia. Your health, age, anesthesia risk, and the surgeon’s expertise are also important. An operation is the only treatment for incarcerated/ strangulated and femoral hernias. Your hernia can be repaired either as an open or laparoscopic approach. The repair can be done by using sutures only or adding a piece of mesh
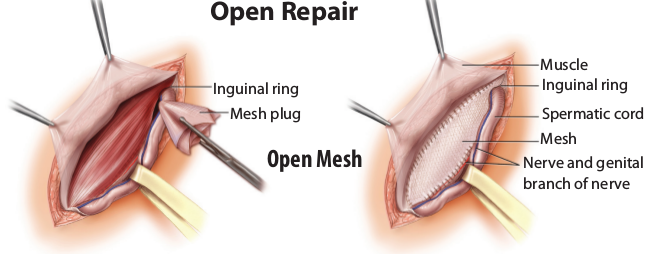
The surgeon makes an incision near the hernia site, and the bulging tissue is gently pushed back into the abdomen. Sutures or mesh are used to close the muscle.
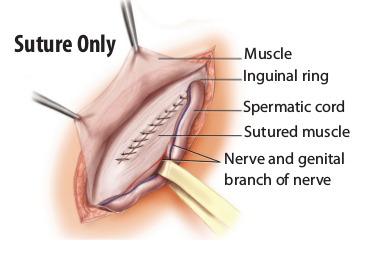
For a suture-only repair: The hernia sac is removed. Then the tissue along the muscle edge is sewn together. The umbilicus is then fixed back to the muscle. This procedure is often used for small defects.
For an open mesh repair: The hernia sac is removed. Mesh is placed beneath the hernia site. The mesh is attached using sutures sewn into the stronger tissue surrounding the hernia. The mesh extends 3 to 4 cm beyond the edges of a hernia. The umbilicus is fixed back to the muscle. Mesh is often used for large hernia repairs and reduces the risk that a hernia will come back again.
The surgeon will make several small punctures or incisions in the abdomen. Ports or trocars (hollow tubes) are inserted into the openings. Surgical tools and a lighted camera are placed into the ports. The abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to make it easier for the surgeon to see a hernia. Mesh may be sutured or fixed with staples to the muscle around the hernia site. The port openings are closed with sutures, surgical clips, or glue.
Watchful waiting is an option if you have an inguinal hernia with no symptoms. Hernia incarceration occurred in 1.8 per is often used for large hernia repairs 1,000 men who waited longer than 2 years to have a repair. Femoral hernias should always be repaired because of the high-risk sutures, staples, or surgical glue. (400 of 1,000) of incarceration and bowel within 2 years of diagnosis. sac is removed. Then the tissue along the muscle edge is sewn together. Trusses or belts can help manage the symptoms This procedure is often used for of a hernia by applying pressure at the site. A strangulated or infected hernias or truss requires correct fitting and small defects (less than 3 cm). complications include testicular nerve Open Hernia Repair Nonsurgical Treatment damage and incarceration may result.
A laparoscopic repair of inguinal a hernia may result in less pain and numbness, lower infection rate, and faster return to normal activity when compared with open surgery. Laparoscopic repair may lengthen the operative time and may cost more. A recurrence from a previous open hernia repair is best repaired laparoscopically because you avoid scar tissue from previous incisions. Laparoscopic repair of a bilateral (both sides of the groin) inguinal hernias also resulted in the earlier return to work then open repairs. The risk of complications increases for both the open and laparoscopic procedure if the a hernia extends into the scrotum.
The type of operation depends on hernia size and location, and if it is a repeat hernia. Your health, age, anesthesia risk, and the surgeon’s expertise are also important. An operation is the only treatment for incarcerated/ strangulated and femoral hernias. Your hernia can be repaired either as an open or laparoscopic approach. The repair can be done by using sutures only or adding a piece of mesh
The surgeon makes an incision near the hernia site, and the bulging tissue is gently pushed back into the abdomen. Sutures or mesh are used to close the muscle.
For a suture-only repair: The hernia sac is removed. Then the tissue along the muscle edge is sewn together. The umbilicus is then fixed back to the muscle. This procedure is often used for small defects.
For an open mesh repair: The hernia sac is removed. Mesh is placed beneath the hernia site. The mesh is attached using sutures sewn into the stronger tissue surrounding the hernia. The mesh extends 3 to 4 cm beyond the edges of a hernia. The umbilicus is fixed back to the muscle. Mesh is often used for large hernia repairs and reduces the risk that a hernia will come back again.
The surgeon will make several small punctures or incisions in the abdomen. Ports or trocars (hollow tubes) are inserted into the openings. Surgical tools and a lighted camera are placed into the ports. The abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to make it easier for the surgeon to see a hernia. Mesh may be sutured or fixed with staples to the muscle around the hernia site. The port openings are closed with sutures, surgical clips, or glue.
Watchful waiting is an option if you have an inguinal hernia with no symptoms. Hernia incarceration occurred in 1.8 per is often used for large hernia repairs 1,000 men who waited longer than 2 years to have a repair. Femoral hernias should always be repaired because of the high-risk sutures, staples, or surgical glue. (400 of 1,000) of incarceration and bowel within 2 years of diagnosis. sac is removed. Then the tissue along the muscle edge is sewn together. Trusses or belts can help manage the symptoms This procedure is often used for of a hernia by applying pressure at the site. A strangulated or infected hernias or truss requires correct fitting and small defects (less than 3 cm). complications include testicular nerve Open Hernia Repair Nonsurgical Treatment damage and incarceration may result.
A laparoscopic repair of inguinal a hernia may result in less pain and numbness, lower infection rate, and faster return to normal activity when compared with open surgery. Laparoscopic repair may lengthen the operative time and may cost more. A recurrence from a previous open hernia repair is best repaired laparoscopically because you avoid scar tissue from previous incisions. Laparoscopic repair of a bilateral (both sides of the groin) inguinal hernias also resulted in the earlier return to work then open repairs. The risk of complications increases for both the open and laparoscopic procedure if the a hernia extends into the scrotum.
Bring a list of all of the medications and vitamins that you are taking. Your medication may have to be adjusted before your operation. Some medications can affect your recovery and response to the anesthesia. Most often you will take your morning medication with a sip of water.
Let your anesthesia provider know if you have allergies, neurologic disease (epilepsy, stroke), heart disease, stomach problems, lung disease (asthma, emphysema), endocrine disease (diabetes, thyroid conditions), or loose teeth; if you smoke, drink alcohol, use drugs, or take any herbs or vitamins; or if you have a history of nausea and vomiting with anesthesia. If you smoke, you should let your surgical team know and you should plan to quit. Quitting before your surgery can decrease your rate of respiratory and wound complications and increase your chances of staying smoke- free for life.
If you have local anesthesia, you will usually go home the same day. You may stay overnight if you had a repair of a large or incarcerated hernia, laparoscopic repair with a longer anesthesia time, postanesthesia issues such as severe nausea and vomiting, or you are unable to pass urine.
An identification (ID) bracelet and allergy bracelet with your name and hospital/clinic number will be placed on your wrist. These should be checked by all health team members before they perform any procedures or give you medication. Your surgeon will mark and initial the operation site.
An intravenous line (IV) will be started to give you fluids and medication. For general anesthesia, you will be asleep and pain-free during the operation. A tube may be placed in your throat to help you breathe during the operation. For spinal anesthesia, a small needle with medication will be placed on your back alongside your spinal column. You will be awake during the operation but pain-free.
You will be moved to a recovery room where your heart rate, breathing rate, oxygen saturation, blood pressure, and urine output will be closely watched. Be sure that all visitors wash their hands.
Movement and deep breathing after your operation can help prevent postoperative complications such as blood clots, fluid in your lungs, and pneumonia. Every hour, take 5 to 10 deep breaths and hold each breath for 3 to 5 seconds. When you have an operation, you are at risk of getting blood clots because of not moving during anesthesia. The longer and more complicated your surgery, the greater the risk. This risk is decreased by getting up and walking 5 to 6 times per day, wearing special support stockings or compression boots on your legs, and, for high-risk patients, taking a medication that thins your blood.
Avoid straining with bowel movements by increasing the fiber in your diet with high- fiber foods or over-the-counter medicines (like Metamucil® and FiberCon®). Be sure you are drinking 8 to 10 glasses of water each day
The amount of pain is different for each person. Some people need only 1 to 3 doses of pain control medication, while others need more. The new medicine you will need after your operation is for pain control, and your doctor will advise how much you should take. You can use throat lozenges if you have sore throat pain from the tube placed in your throat during your anesthesia.
Contact your surgeon if you have:
Pain that continues one year after inguinal hernia repair is reported as 110 of 1,000 patients, with moderate/severe pain reported in 17 of 1,000. 80% of patients with severe groin pain had pain before the operation. The pain decreased by 50% in one year. The incidence of pain is higher in women than in men. Pain was higher when heavy versus light- weight mesh was used. Most studies do not report a difference in chronic pain between open versus laparoscopic repair.
Everyone reacts to pain in a different way. A scale from 0 to 10 is used to measure pain. At a “0,” you do not feel any pain. A “10” is the worst pain you have ever felt. Following a laparoscopic procedure, pain is sometimes felt in the shoulder. This is due to the gas inserted into your abdomen during the procedure. Moving and walking helps to decrease the gas and the right shoulder pain. Extreme pain puts extra stress on your body at a time when your body needs to focus on healing. Do not wait until your pain has reached a level “10” or is unbearable before telling your doctor or nurse. It is much easier to control pain before it becomes severe
Narcotics are used for severe pain. Possible side effects of narcotics are sleepiness; lowered blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing rate; skin rash and itching; constipation; nausea; and difficulty urinating. Some examples of narcotics include morphine, oxycodone (Percocet®/Percodan), and hydromorphone (Dilaudid). Medications can be given to control many of the sides effects of narcotics
most non-opioid analgesics are classified as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They are used to treat mild pain and inflammation or combined with narcotics to treat severe pain. Possible side effects of NSAIDs are stomach upset, bleeding in the digestive tract, and fluid retention. These side effects usually are not seen with short- term use. Let your doctor know if you have heart, kidney, or liver problems. Examples of NSAIDs include ibuprofen, Motrin, Aleve, and Toradol (given as a shot)
Distraction helps you focus on other activities instead of your pain. Listening to music, playing games, or other engaging activities can help you cope with mild pain and anxiety.
Guided imagery helps you direct and control your emotions. Close your eyes and gently inhale and exhale. Picture yourself in the center of somewhere beautiful. Feel the beauty surrounding you and your emotions coming back to your control. You should feel calmer.

User visits the website and navigates to the "Appointment Booking" section.
After completing the form, the user submits their appointment request.
If the requested slot is available, the administrative staff confirms appointment.